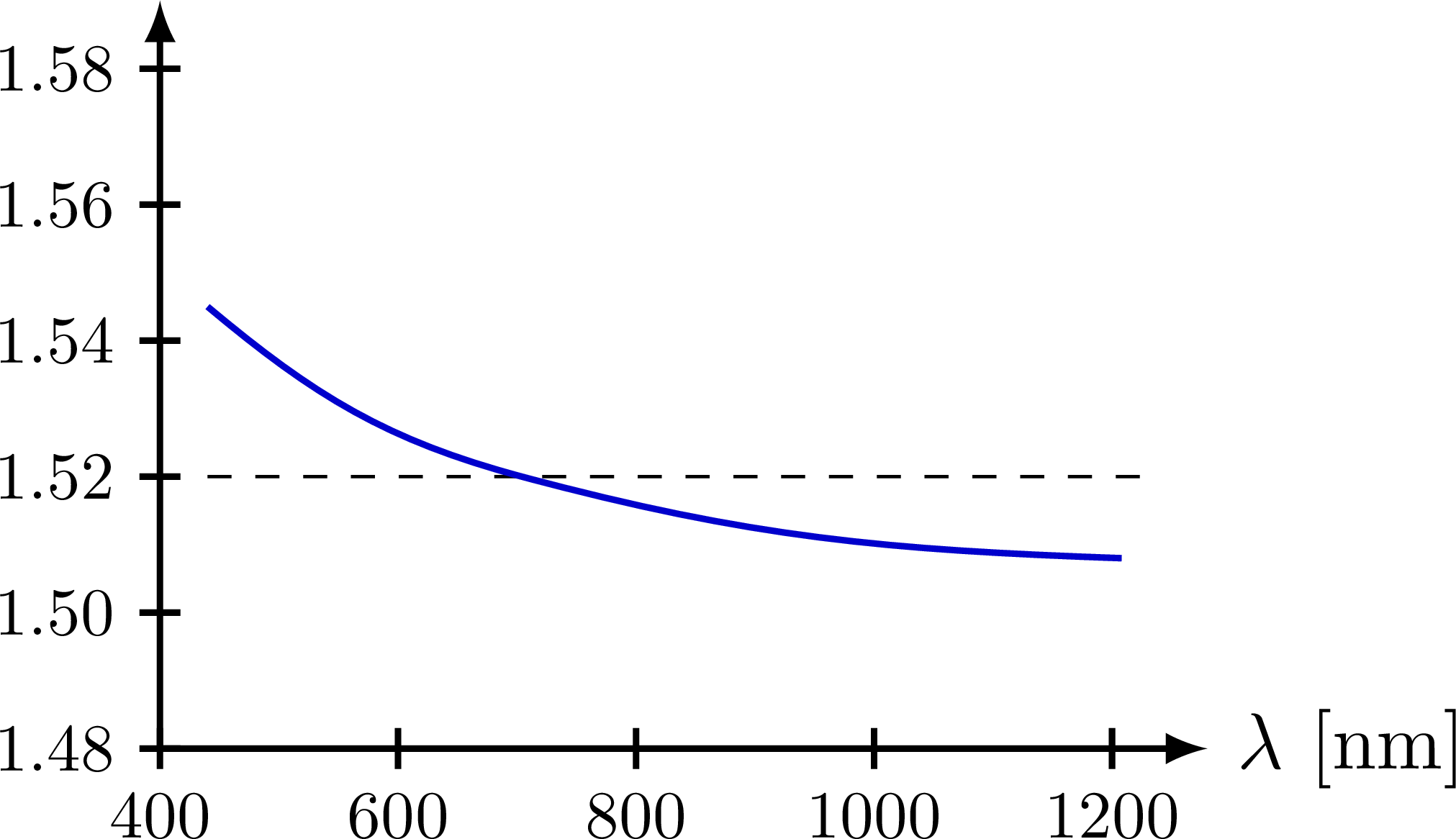
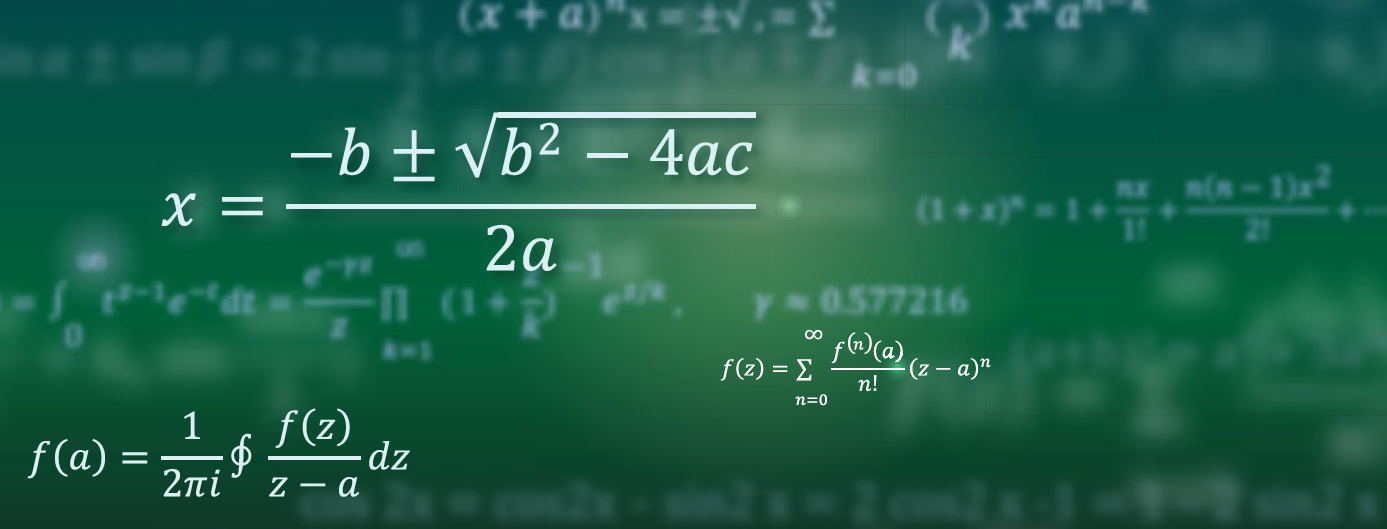Dispersion in a prism due to refraction. Incident white light is converted into a rainbow, as reported by Newton in 1666, or as shown on Pink Floyd’s Dark Side of the Moon (1973).
For more related figures, please see the Optics category.
Edit and compile if you like:
% Author: Izaak Neutelings (June 2020)
% Inspiration:
% https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-Refractive-index-and-b-dispersion-of-bulky-soft-glasses-NC21-LLF1-SF6-and-F2-As_fig1_236110630
% https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11082-014-9979-y
\documentclass[border=3pt,tikz]{standalone}
\usepackage{siunitx}
\usetikzlibrary{calc}
\usetikzlibrary{intersections}
\usetikzlibrary{fadings}
\tikzset{>=latex} % for LaTeX arrow head
\colorlet{myblue}{blue!80!black}
\colorlet{myred}{black!50!red}
\colorlet{glasscol}{blue!10}
\tikzstyle{glass}=[top color=glasscol!90!black,bottom color=glasscol!90!black,middle color=glasscol,shading angle=40]
\begin{document}
%% PRISM + REFRACTION
%\begin{tikzpicture}
% \def\N{6}
% \def\L{2.8}
% \def\na{1.0} % air
% \def\angi{50}
% \coordinate (O) at (0,0);
% \coordinate (R) at (\L,0);
% \coordinate (T) at (60:\L);
% \coordinate (I) at (60:0.5*\L);
%
% % MEDIUM
% \draw[line width=0.8,blue] (I)++(150+\angi:0.3*\L) -- (I) --++ (\angi-30:0.007*\L);
% \draw[line width=0.6,white] (I)++(150+\angi:0.3*\L) -- (I) --++ (\angi-30:0.007*\L);
% \fill[glass] (O) -- (T) -- (R) -- cycle;
% \path[name path=side] (T) -- (R);
%
% % LIGHT BEAMS
% % https://tex.stackexchange.com/questions/230227/creating-a-rainbow-color-macro
% \foreach \i [evaluate={
% \ng=1.6-\i*0.2/\N;
% \lamb=410+\i*320/\N;
% %\len=1.5+\i*0.8/\N;
% \angr=asin(\na/\ng*sin(\angi));
% \angR=asin(\ng/\na*sin(60-\angr));
% \dang=-30+\i*60/\N;}] in {0,...,\N}{
% \definecolor{tmpcol}{wave}{\lamb}
% \colorlet{mycol}[rgb]{tmpcol}
% \path[name path=beam1] (I) --++ (-30+\angr:0.8*\L);
% \draw[mycol,name intersections={of=side and beam1,name=f}] %wave={\len}
% (I)++(\dang:0.0028*\L) -- (f-1) --++ (30-\angR:0.4*\L); %node[scale=0.3] {\angR};
% }
% %\foreach \i in {1,2}{
% % \draw[line width=0.59,white,path fading=east] (I)++(20:0.002*\L) --++ (1:0.08*\L);
% % \draw[line width=0.59,white,path fading=east] (I)++(20:0.002*\L) --++ (1:0.03*\L);
% %}
% \coordinate (IT) at ($(I)+(60:0.006*\L)$);
% \fill[white,path fading=east]
% (IT) --++ (-120:0.012*\L) --++ (-1.3:0.10*\L) --++ (80:0.018*\L) -- cycle;
% \fill[white,path fading=east]
% (IT) --++ (-120:0.012*\L) --++ (-1.3:0.06*\L) --++ (80:0.0148*\L) -- cycle;
%
%\end{tikzpicture}
% PRISM + REFRACTION
\begin{tikzpicture}
\def\N{200} % number of rainbow rays
\def\L{2.8}
\def\na{1.0} % air
\def\angi{50}
\coordinate (O) at (0,0);
\coordinate (R) at (\L,0);
\coordinate (T) at (60:\L);
\coordinate (I) at (60:0.5*\L);
% MEDIUM
\draw[line width=0.8,blue] (I)++(150+\angi:0.3*\L) -- (I) --++ (\angi-30:0.01*\L);
\draw[line width=0.6,white] (I)++(150+\angi:0.3*\L) -- (I) --++ (\angi-30:0.01*\L);
\fill[glass] (O) -- (T) -- (R) -- cycle;
\path[name path=side] (T) -- (R);
% LIGHT BEAMS
% https://tex.stackexchange.com/questions/230227/creating-a-rainbow-color-macro
\begin{scope}
\coordinate (IT) at ($(I)+(60:0.006*\L)$);
\clip (O) -- (T) -- (1.08*\L,0.45*\L) to[out=-35,in=20,looseness=1]
(1.04*\L,0.2*\L) -- (R) -- cycle;
\foreach \i [evaluate={
\f=\i/\N;
\ng=1.6-\f*0.2;
\lamb=410+\f*320;
\angr=asin(\na/\ng*sin(\angi));
\angR=asin(\ng/\na*sin(60-\angr));
\dl=0.0108*(1-\f)*\L;}] in {0,...,\N}{
\definecolor{tmpcol}{wave}{\lamb}
\colorlet{mycol}[rgb]{tmpcol}
\path[name path=beam1] (I) --++ (-30.1+\angr:0.8*\L);
\path[name path=beam2] (I) --++ (-30.0+\angr:0.8*\L);
\coordinate (IT2) at ($(I)+(57:0.005*\L)+(-120:\dl)$);
\fill[mycol,name intersections={of=side and beam1,name=t},
name intersections={of=side and beam2,name=b}] %wave={\len}
(IT2) -- (t-1) -- ($(t-1)+(30.0-\angR:0.4*\L)$)
-- ($(b-1)+(30.1-\angR:0.4*\L)$) -- (b-1) -- ($(IT2)+(-120:-0.001*\L)$); %node[scale=0.3] {\angR};
}
\end{scope}
\fill[white,path fading=east]
(IT) --++ (-120:0.012*\L) --++ (-1.3:0.06*\L) --++ (80:0.015*\L) -- cycle;
\fill[white,path fading=east]
(IT) --++ (-120:0.012*\L) --++ (-1.3:0.10*\L) --++ (80:0.018*\L) -- cycle;
\end{tikzpicture}
% REFRACTION
\begin{tikzpicture}
\def\Nx{4}
\def\Ny{5}
\def\xmax{4.2}
\def\ymax{3}
\def\nave{0.4*\ymax}
\coordinate (L) at (0.05*\xmax,0.65*\ymax);
\coordinate (M) at (0.38*\xmax,0.40*\ymax);
\coordinate (R) at (1.01*\xmax,0.28*\ymax);
\def\tick#1#2{\draw[thick] (#1) ++ (#2:0.03*\ymax) --++ (#2-180:0.06*\ymax)}
% AXES
\draw[->,thick] (0,0) -- (1.1*\xmax,0) node[right] {$\lambda$ [\si{nm}]};
\draw[->,thick] (0,0) -- (0,1.1*\ymax);
\foreach \i [evaluate={\x=\i*\xmax/\Nx;\lamd=int(400+\i*200)}] in {0,...,\Nx}{
\tick{\x,0}{90} node[below,scale=0.85] {$\lamd$};
}
\pgfkeys{/pgf/number format/precision=2} % decimal precision
\foreach \i [evaluate={\y=\i*\ymax/\Ny;}] in {0,...,\Ny}{
\pgfmathparse{1.48+\i*0.02}
\pgfmathroundtozerofill{\pgfmathresult}
\pgfmathsetmacro\n{\pgfmathresult}
\tick{0,\y}{0} node[left,scale=0.85] {$\n$};
}
% LINE
\draw[dashed] (0.05*\xmax,\nave) -- (1.05*\xmax,\nave);
\draw[myblue,thick]
(L) to[out=-40,in=165,looseness=1] (M)
to[out=-15,in=178,looseness=1] (R);
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{document}Click to download: optics_prism.tex • optics_prism.pdf
Open in Overleaf: optics_prism.tex