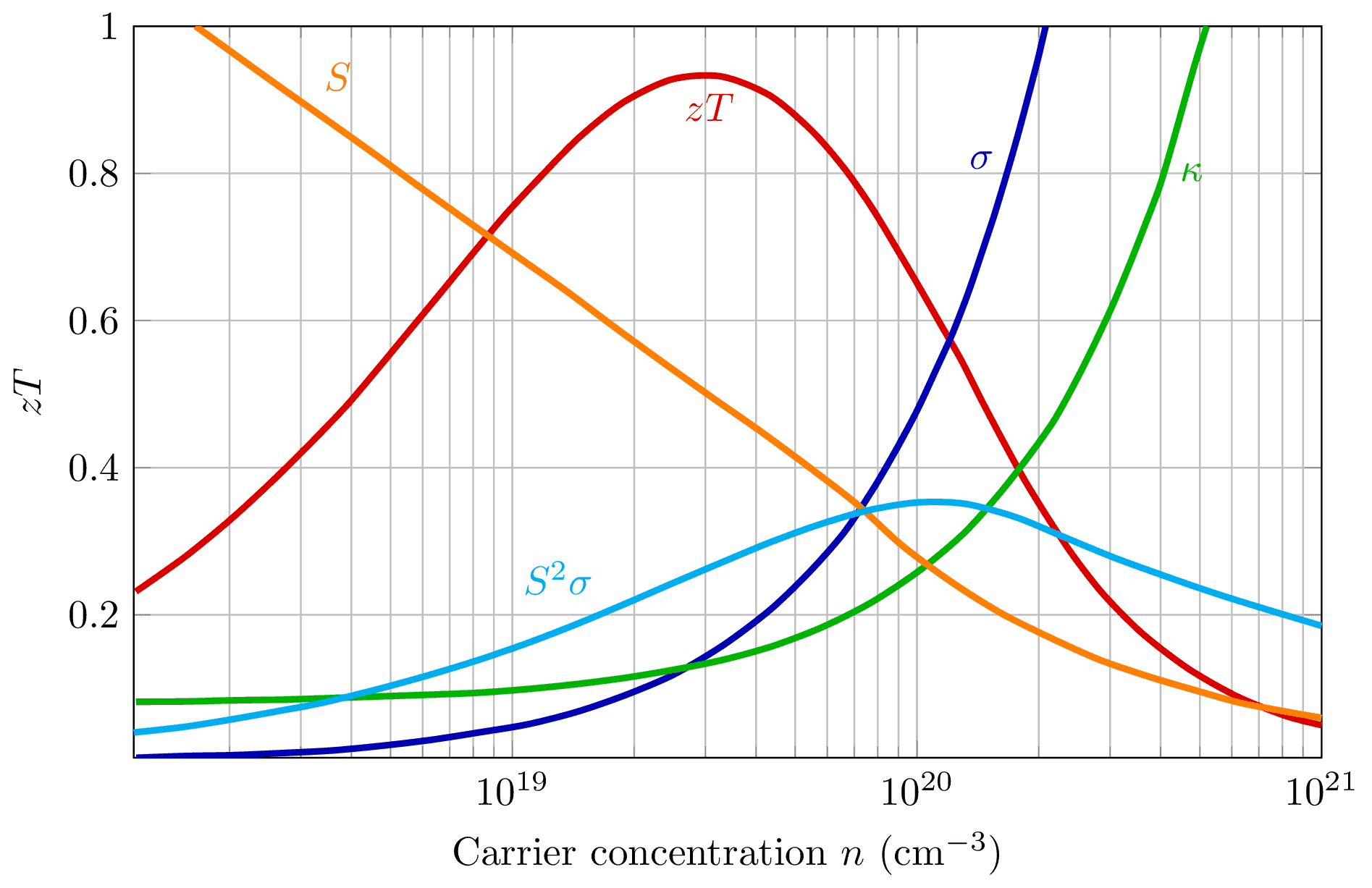
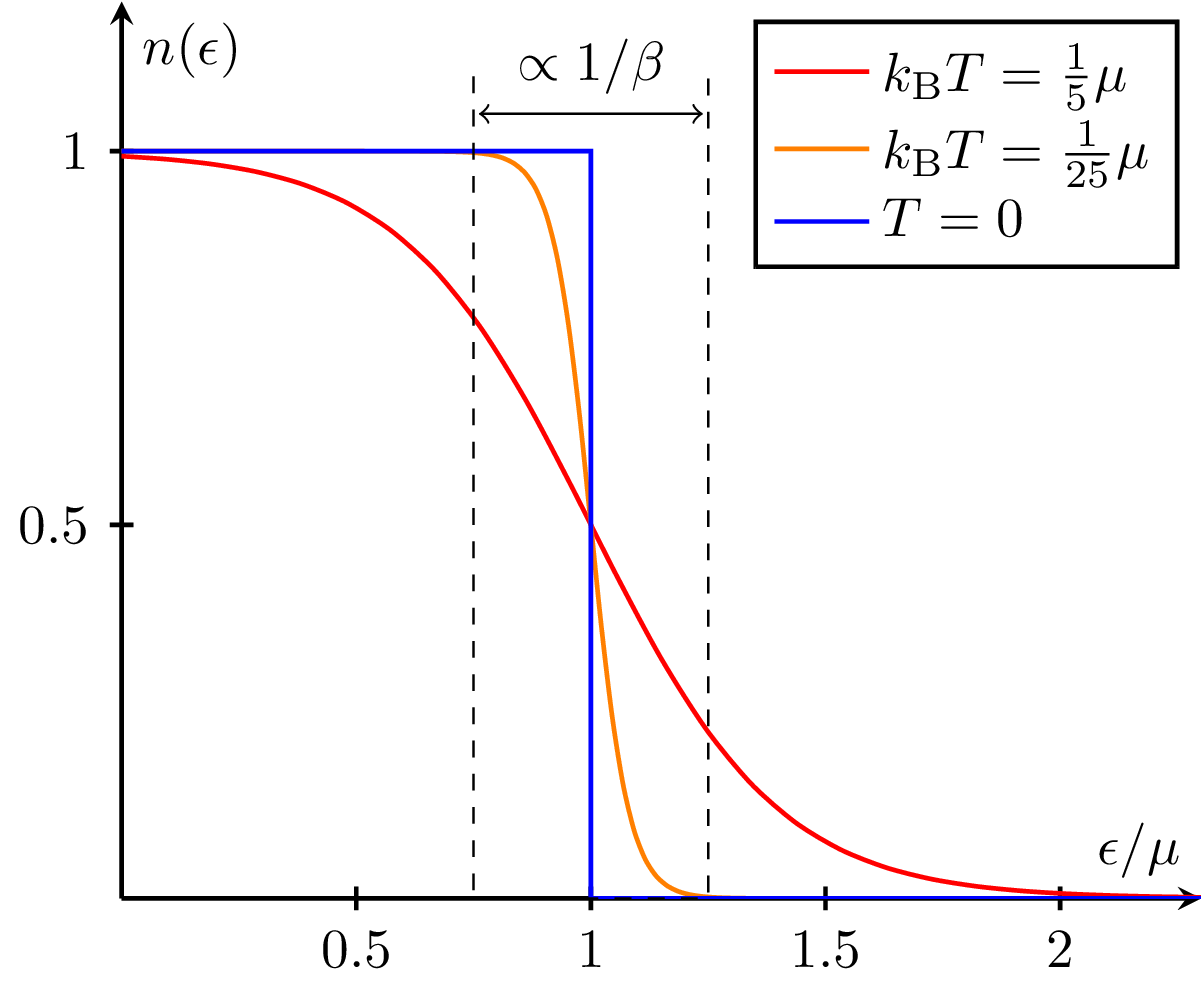
Thermoelectric figure of merit $zT$ vs carrier concentration $n$ for \ch{Bi2Te3} based on empirical data in ref.~\cite{rowe_alpha-sigma_1995}. Tuning $n$ for optimal $zT$ involves a compromise between thermal conductivity $\kappa$, Seebeck coefficient $S$ and electrical conductivity $\sigma$.
Increasing the electrical conductivity $\sigma$ not only produces an increase in the electronic thermal conductivity $\kappa_\text{el}$ but also usually decreases the Seebeck coefficient $S$. This makes optimal $\zT$ difficult to achieve. Plot scales are $\kappa/\si{\watt\per\meter\per\kelvin} \in [0,10]$, $S/\si{\micro\volt\per\kelvin} \in [0,500]$, $\sigma/\si{\per\ohm\per\centi\meter} \in [0,5000]$.
Edit and compile if you like:
% Thermoelectric figure of merit $zT$ vs carrier concentration $n$ for \ch{Bi2Te3} based on empirical data in ref.~\cite{rowe_alpha-sigma_1995}. Tuning $n$ for optimal $zT$ involves a compromise between thermal conductivity $\kappa$, Seebeck coefficient $S$ and electrical conductivity $\sigma$. Increasing the electrical conductivity $\sigma$ not only produces an increase in the electronic thermal conductivity $\kappa_\text{el}$ but also usually decreases the Seebeck coefficient $S$. This makes optimal $\zT$ difficult to achieve. Plot scales are $\kappa/\si{\watt\per\meter\per\kelvin} \in [0,10]$, $S/\si{\micro\volt\per\kelvin} \in [0,500]$, $\sigma/\si{\per\ohm\per\centi\meter} \in [0,5000]$.
\documentclass[tikz]{standalone}
\usepackage{pgfplots,siunitx}
\pgfplotsset{compat=newest}
\begin{document}
\begin{tikzpicture}
\begin{axis}[
xmode=log,
domain=1e17:1e21,
ymax=1,
enlargelimits=false,
ylabel=$zT$,
xlabel=Carrier concentration $n$ (\si{\per\centi\meter\cubed}),
grid=both,
width=12cm,
height=8cm,
decoration={name=none},
]
\addplot [ultra thick, smooth, red!85!black] coordinates {
(1.174e+18, 0.2317)
(1.551e+18, 0.2787)
(2.016e+18, 0.3300)
(2.549e+18, 0.3816)
(3.171e+18, 0.4332)
(3.891e+18, 0.4842)
(4.697e+18, 0.5373)
(5.623e+18, 0.5892)
(6.714e+18, 0.6404)
(8.017e+18, 0.6923)
(9.650e+18, 0.7450)
(1.178e+19, 0.7963)
(1.461e+19, 0.8486)
(1.878e+19, 0.8964)
(2.481e+19, 0.9278)
(3.279e+19, 0.9318)
(4.334e+19, 0.9057)
(5.515e+19, 0.8571)
(6.662e+19, 0.8045)
(7.767e+19, 0.7519)
(8.859e+19, 0.7000)
(1.008e+20, 0.6476)
(1.143e+20, 0.5953)
(1.290e+20, 0.5449)
(1.447e+20, 0.4906)
(1.628e+20, 0.4374)
(1.837e+20, 0.3850)
(2.101e+20, 0.3327)
(2.436e+20, 0.2799)
(2.887e+20, 0.2281)
(3.594e+20, 0.1753)
(4.674e+20, 0.1271)
(6.178e+20, 0.08917)
(8.167e+20, 0.06240)
(1e+21, 0.05)
} node[pos=0.48, anchor=north] {$zT$};
\addplot [ultra thick, smooth, blue!70!black] coordinates {
(1.176e+18, 0.005689)
(1.554e+18, 0.008070)
(2.054e+18, 0.009285)
(2.714e+18, 0.01216)
(3.587e+18, 0.01561)
(4.740e+18, 0.02190)
(6.264e+18, 0.02984)
(8.277e+18, 0.04013)
(1.094e+19, 0.05127)
(1.445e+19, 0.06820)
(1.910e+19, 0.09120)
(2.511e+19, 0.1191)
(3.333e+19, 0.1593)
(4.344e+19, 0.2072)
(5.433e+19, 0.2587)
(6.613e+19, 0.3123)
(7.852e+19, 0.3739)
(8.925e+19, 0.4266)
(1.001e+20, 0.4779)
(1.110e+20, 0.5310)
(1.224e+20, 0.5824)
(1.335e+20, 0.6359)
(1.441e+20, 0.6893)
(1.551e+20, 0.7425)
(1.660e+20, 0.7960)
(1.767e+20, 0.8478)
(1.876e+20, 0.9009)
(1.986e+20, 0.9532)
(2.08e+20, 1)
} node[pos=0.95, anchor=east] {$\sigma$};
\addplot [ultra thick, smooth, green!70!black] coordinates {
(1.175e+18, 0.08187)
(1.553e+18, 0.08218)
(2.053e+18, 0.08379)
(2.713e+18, 0.08472)
(3.585e+18, 0.08684)
(4.738e+18, 0.08916)
(6.261e+18, 0.09142)
(8.274e+18, 0.09411)
(1.093e+19, 0.09912)
(1.445e+19, 0.1059)
(1.909e+19, 0.1145)
(2.523e+19, 0.1256)
(3.334e+19, 0.1391)
(4.405e+19, 0.1576)
(5.821e+19, 0.1830)
(7.691e+19, 0.2164)
(1.016e+20, 0.2605)
(1.302e+20, 0.3102)
(1.589e+20, 0.3629)
(1.882e+20, 0.4143)
(2.181e+20, 0.4641)
(2.472e+20, 0.5181)
(2.764e+20, 0.5714)
(3.066e+20, 0.6246)
(3.363e+20, 0.6780)
(3.669e+20, 0.7310)
(3.981e+20, 0.7826)
(4.273e+20, 0.8389)
(4.560e+20, 0.8942)
(4.868e+20, 0.9493)
(5.2e+20, 1)
} node[pos=0.95, anchor=west] {$\kappa$};
\addplot [ultra thick, smooth, orange] coordinates {
(1.65e+18, 1)
(1.931e+18, 0.9729)
(2.553e+18, 0.9248)
(3.375e+18, 0.8777)
(4.462e+18, 0.8302)
(5.899e+18, 0.7816)
(7.745e+18, 0.7351)
(1.031e+19, 0.6866)
(1.363e+19, 0.6397)
(1.802e+19, 0.5897)
(2.382e+19, 0.5412)
(3.149e+19, 0.4937)
(4.162e+19, 0.4471)
(5.503e+19, 0.3977)
(7.117e+19, 0.3500)
(9.181e+19, 0.2944)
(1.224e+20, 0.2436)
(1.618e+20, 0.2019)
(2.138e+20, 0.1687)
(2.826e+20, 0.1389)
(3.736e+20, 0.1161)
(4.938e+20, 0.09646)
(6.321e+20, 0.08022)
(8.578e+20, 0.06624)
(1e+21, 0.06)
} node[pos=0.1, anchor=south west] {$S$};
\addplot [ultra thick, smooth, cyan] coordinates {
(1.159e+18, 0.04006)
(1.532e+18, 0.04739)
(2.025e+18, 0.05790)
(2.676e+18, 0.06974)
(3.386e+18, 0.08033)
(4.675e+18, 0.09928)
(6.179e+18, 0.1176)
(8.168e+18, 0.1379)
(1.080e+19, 0.1608)
(1.427e+19, 0.1864)
(1.886e+19, 0.2142)
(2.492e+19, 0.2430)
(3.294e+19, 0.2713)
(4.353e+19, 0.2989)
(5.754e+19, 0.3230)
(7.605e+19, 0.3422)
(1.005e+20, 0.3528)
(1.314e+20, 0.3509)
(1.757e+20, 0.3326)
(2.327e+20, 0.3049)
(3.071e+20, 0.2777)
(4.061e+20, 0.2535)
(5.369e+20, 0.2304)
(7.098e+20, 0.2095)
(1e+21, 0.185)
} node[pos=0.4, anchor=south east] {$S^2 \sigma$};
\end{axis}
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{document}
Click to download: zt-vs-n.tex
Open in Overleaf: zt-vs-n.tex
This file is available on tikz.netlify.app and on GitHub and is MIT licensed.
See more on the author page of Janosh Riebesell..